Use MySql with .Net Core 3.1 & .NET 5
Possibility of using MySQL (or MariaDB) with .Net Core opens an opportunity to use open-source & free database. Moreover, one can take advantage of .Net Core or .Net 5 being cross-platform by bypassing all Microsoft's paid services! Yes, Linux hosting with one of the open-source & free database.
MySQL is technically an open-source database. However, under Oracle, MySQL now has proprietary, closed-source modules. MariaDB, being a MySQL fork, is a good alternative. MariaDB 5.5 offers all of the MySQL 5.5 features1.
In this post, I will show how we can use Entity Framework 5.0 Code First approach to create tables in a MySQL database.
Project setup
The advantage of using .Net Core again is use of light-weight Visual Studio Code (perhaps one of the best open-source free code editor) with millions of plugins. Great for Linux as Visual Studio is available only for Windows and Mac. I will be using Visual Studio 2019 Community Edition (free) and MySQL 5.7.
We will be using dotnet new command to scaffold builtin template. It can also be done using GUI in Visual Studio.
- Create a folder for the project.
- Open command prompt, and go to the folder.
- Type
dotnet new --list. It shows a list of available templates. - We will be using ASP.NET CORE Web API template targeting .Net Core 3.1.
- Type
D:\DotNetCoreMySQL>dotnet new webapi --framework netcoreapp3.1. Check here for more template version. - The command will create a project in the given folder. Remember, it does NOT create a Solution like Visual Studio does. One need to run a command explicitly to create solution. I will be skipping it.
This post assumes all the dependencies are installed. .NET Core SDK or Runtime (at least 3.1) (can check installed version using
dotnet --version), MySQL and Visual Studio or Visual Studio Code (prepare to write more code).
Go to the project folder, right-click PROJECT_NAME.csproj file, and choose 'Open With Visual Studio'
Install Entity Framework Core 5.0
Again, we can install package from Nuget using Visual Studio GUI. However, it's handy to do using CLI in Package Manager Console.
Tips: Open nuget.org so that we can copy CLI from there
- Go to nuget.org and search EF Core or follow this link
- Click Package Manager tab, and click copy icon on right-hand side.
- Pase it in Visual Studio's Package Manager Console.
- Install EntityFrameworkCore Design from here
- We also need EF Core Command Line Tools to create migrations, update the database, etc. It's installed on global scope. First check if it's installed by
dotnet ef. If you don't see text EF with Unicorn followed by options then we need to install it on command prompt bydotnet tool install --global dotnet-ef --version 5.0.1
Install Entity Framework Core provider for MySQL
We will be using Pomelo provider over MySql.Data.EntityFrameworkCore. The latter one is official MySQL provider, however, I did not have a good experience with it, so my choice is Pomelo.
- Get the latest (alpha.2) version from here
- Paste the copied code to Package Manager Console.
Create a database in MySQL (I use MySQL Workbench)
I am not going to show guidelines regarding creating a database and a user in MySQL. MySQL Workbench cannot be compared with SQL Server Management Studio but quite easy to use.
- I am using a database mysqldotnet and a user mysqldotnetuser for this database in this example.
Create a model to generate a table.
- Create a folder Models at the root of the project.
- Add a class to the folder, let say User
- Now, let's define our model.
By default, EF Core will pluralize the generated table name. For example, User will be mapped as Users in the database. To have singularize name, decorate class with the attribute
[Table("User")]
[Table("User")]
public class User
{
[Key]
[DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity)]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
[MaxLength(50)]
public string FirstName { get; set; }
[Required]
[MaxLength(50)]
public string LastName { get; set; }
[Required]
[MaxLength(250)]
public string Address { get; set; }
[Required]
[MaxLength(50)]
public string Country { get; set; }
[MaxLength(15)]
public int Mobile { get; set; }
}
Create DBContext
Now, DBContext (database context class) is the main class that coordinates Entity Framework functionality for a given data model. In other words, DBContext looks the models and generates corresponding database tables.
It's good idea to have database related operations in a separate project. But for the sake of simplicity, I am doing on the same project. This approach is not recommended.
- Create a folder at the root of the project, let's say Data.
- Create a DbContext derived class inside the newly created folder, let's say DotNetCoreMySQLContext
- Specify the entities to be included in the data model by creating DbSet property like
public DbSet<User> Users { get; set; }.
The DbContext derived DotNetCoreMySQLContext looks like this:
public class DotNetCoreMySQLContext : DbContext
{
public DotNetCoreMySQLContext(DbContextOptions<DotNetCoreMySQLContext> options) : base(options) {}
public DbSet<User> User { get; set; }
}
Add connection string
- We need to tell our app where to find our database.
- Unlike .net framework, connection strings are specified in appsettings.json. There is no web.config.
- Then we have to reference the connection string from Startup.cs.
appsettings.json
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DotNetCoreMySQLAppConnection": "server=localhost; port=3306; database=mysqldotnet; user=mysqldotnetuser; password=Pa55w0rd!; Persist Security Info=false; Connect Timeout=300"
}
It's always a bad idea to store password in appsettings.json file. Even if we are pushing in our private repository. This can be avoided by using user secrets. Again, for the sake of simplicity, I am using plain password. However, user secrets is a good topic for a blog itself!
Inject connection string in Startup.cs
ConfigureServices method from startup.cs
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
string dbConnectionString = Configuration.GetConnectionString("DotNetCoreMySQLAppConnection");
services.AddDbContext<DotNetCoreMySQLContext>(opt => opt.UseMySql(dbConnectionString, ServerVersion.AutoDetect(dbConnectionString)));
services.AddControllers();
}
This line services.AddDbContext<DotNetCoreMySQLContext>(opt => opt.UseMySql(dbConnectionString, ServerVersion.AutoDetect(dbConnectionString))) tells the app to use MySQL provider and our context class with the connection string from appsettings.json.
Create migration and update database
Now, we have setup everything to use Code-First approach to create tables in the database. Entity Framework keep tracks of all models through migrations. Every time, we update or create model, we need to do so my making a unique migration. These migrations becomes a sort of record and they can be used to roll-back in the event of an error.
- Create first migration by typing following command in Package Manager Console
PM> dotnet ef migrations add FirstMigration
Build started...
Build succeeded.
Done. To undo this action, use 'ef migrations remove'
PM>
EF creates a folder called Migrations at the root of the project to store all migrations. 2. Apply changes to the database by typing command given below. Remember, MySQL server must be running at this time.
PM> dotnet ef database update
Build started...
Build succeeded.
Done.
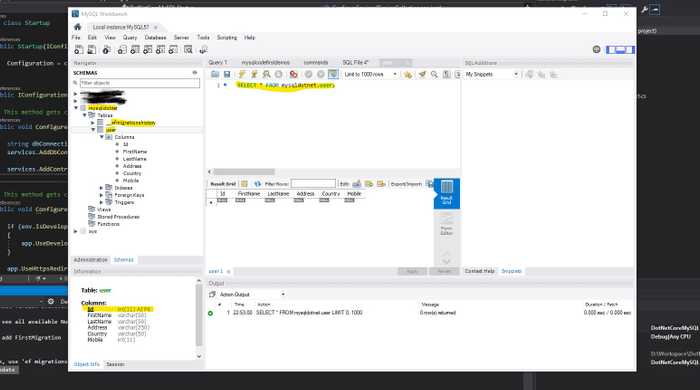
Confirm table creation in the database.
Open MySQL Workbench (or your SQL editor) and confirm the creation of the table.
Using .NET 5.0
Change the Target Framework by right-clicking on the Project name. On Application tab choose .Net 5.0 from the Target Framework dropdown. The can also be done by opening PROJECTNAME.csproj_ file in text editor and changing
<TargetFramework>net5.0</TargetFramework>. NOTE: .NET 5 SDK or runtime must be installed.
Testing if it works with .NET 5.0
- Add a new model in the folder Models.
- Add a new migration.
dotnet ef migrations add NewModel - Update database
dotnet ef database udpate
Refresh the database in MySQL to confirm the new table is created.